The importance of being interconnected
Where do I get the electricity I need, if the sun isn't shining and the wind isn't blowing. One answer is to bring it in from places where its still sunny or windy. This might be in a different country, or a distant part of the same country - enter interconnectors.
Summary: At any particular time, a country may produce less or more electricity than is actually needed. Interconnectors allow electricity to flow between a country with excess electricity to one with a deficit - i.e. to the market with higher pricing. The operator of an interconnector makes money through capacity auctions that give customers transmission rights - i.e. the right to use the interconnector.
Why this is important: The shift toward an electricity generation system dominated by renewables brings new challenges for the system operator. One of these is where do I get the electricity I need, if the sun isn't shining and the wind isn't blowing. One answer is to bring it in from places where its still sunny or windy. This might be in a different country, or a distant part of the same country - enter interconnectors.
The big theme: As countries move toward electricity generation systems dominated by renewables, the need for supporting infrastructure becomes greater. This will include battery/long term storage, demand management and interconnectors, which will enable balancing renewable electricity to be brought in from adjacent regions to offset periods of local shortage.

The details
What is an interconnector?
An interconnector is a cable that connects the electricity systems or 'grids' of nearby countries or offshore renewable energy farms, most often offshore wind farms, to a country's grid.
At any particular time, a country may produce less or more electricity than is actually needed. Interconnectors allow electricity to flow between a country with excess electricity to one with a deficit - i.e. to the market with higher pricing. The operator of an interconnector makes money through capacity auctions that give customers transmission rights - i.e. the right to use the interconnector. They would still need to purchase or produce that electricity.
What is the interconnector itself? It is a high voltage transmission cable that can either be overhead, underground or even submarine, either on or buried just beneath the sea bed.
Most power plants generate an alternating current (AC) where the electrons keep switching directions like a wave and most electrical loads (e.g. appliances) run on AC power. Therefore, the majority of transmission lines that are overhead are AC. However AC lines lose power over long distances, so for the kinds of distances that we are talking about with interconnectors, a DC line is more efficient - High Voltage Direct Current or HVDC line. Conversion of that DC current is then needed into AC when it needs to be used.
Electricity grids
An electricity grid is the term used to describe the infrastructure that delivers electricity from where it is generated to where it is used in a safe and reliable manner. Below is a diagram showing what a traditional grid looks like at the high level:
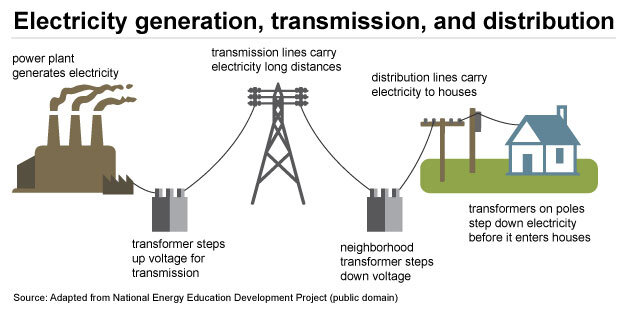
Interconnectors can be particularly useful in connecting renewable electricity generation to a country's grid. For example, interconnectors between Singapore and Malaysia allow up to 100 MW of renewable hydropower from Lao PDR to be imported to Singapore.

Evolution of the grid
As the percentage of renewable electricity generation on the grid increases, the way we store and use electricity will need to change and change dramatically. This will be a massive disruption to the existing system.

Multipurpose Interconnectors (MPI)
We mentioned earlier that an interconnector connects the grids of nearby countries and can also connect offshore renewable energy production plants, typically offshore wind farms, to a country's grid. As offshore generation grows, particularly as those waters are shared by different countries, it would become very costly to connect those farms individually to country grids as well as the accompanying disruption to coastal communities.
MPIs can be used to connect clusters of offshore wind farms to multiple countries providing even more flexibility into the system.
Focus on the UK
The UK grid is run by National Grid plc with the National Grid Electricity System Operator (ESO) operating the transmission system and doing the work to balance supply and demand in real time including coordinating auctions and demand-side responses to reduce peaks in electricity demand.
According to the ESO future energy scenarios, the Average Cold Spell (ACS) peak energy demand or the maximum demand over an average winter, is expected range between about 70 GW and 85 GW by 2035.
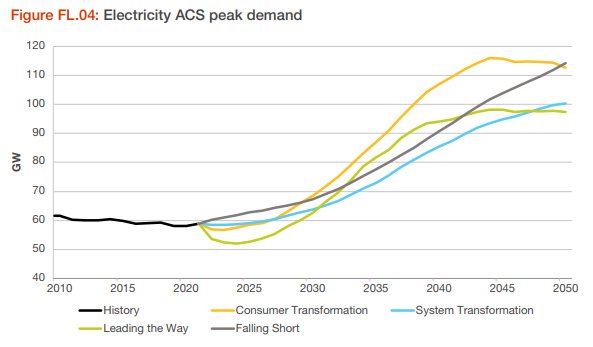
To satisfy that peak demand requires flexibility in the system utilising electricity storage, dispatchable generation (including hydroelectric) and demand side measures including Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) where EVs could provide temporary charge and vice-versa.
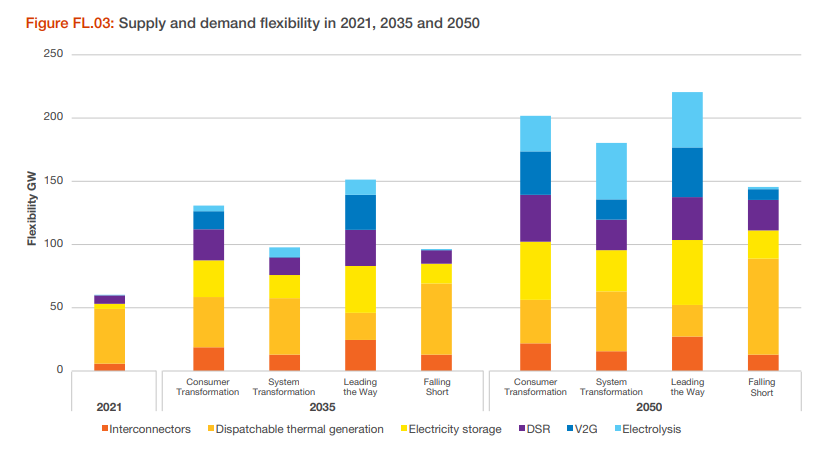
... and of course, interconnectors!
The UK has a number of interconnectors with neighbouring countries that are operational, one that is under construction and a number that are either under review by the authorities or in the early planning stages.
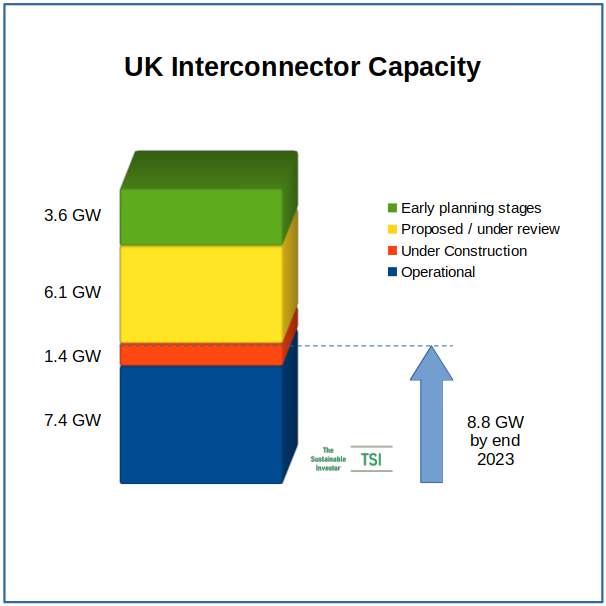
The operational interconnectors are with France (3 GW capacity), Netherlands (1 GW), Belgium (1 GW), Norway (1.4 GW) and Ireland (1 GW in total) with the 1.4 GW Viking Link with Denmark scheduled to go live at the end of 2023.
The UK normally gets cheap nuclear electricity from France (although a number of issues with France's nuclear fleet meant France was a net importer in 2022), gets hydropower from Norway and sends back its surplus renewable electricity which is mostly from offshore wind. Britain's wind farms contributed almost 27 percent of the total electricity generated in 2022.
The 2 GW AQUIND interconnector, a proposal for a privately funded connection with France which was originally rejected by the then Business Secretary Kwasi Karteng had that rejection recently overruled by Judicial Review and is likely to be referred back to the current business secretary Grant Shapps.
A proposed interconnector between the UK and Morocco, part of the Xlinks Power Project, which is still in very early planning and funding stages, would be the longest submarine cable in the world if built at 3,800 km and have a capacity of 3.6 GW.
In future 'Quick Insights' we shall be looking at other countries and their grids and interconnectors.
Something a little more bespoke?
Get in touch if there is a particular topic you would like us to write on. Just for you.
Contact us
Please read: important legal stuff.


